
What follows is a procedure for writing net ionic equations, with an example. Therefore do not appear in a net ionic equation.
Spectator ions are unchanged in the precipitation reaction, and The ion types that do not undergo reaction, and remain in solutionĪfter precipitation, are known as spectator ions. (the products) is known as a net ionic equation. Reactants) and the ionic compound that forms the precipitate Reaction that involves only the ionic species that react (the When a precipitation reaction occurs, a chemical equation for the precipitation Sodium acetate is soluble and remains in solution. Lead iodide actually forms a bright yellow solid. Lead iodide is insoluble and will precipitate. Solutions of lead acetate and sodium iodide are mixed. No precipitation reaction should occur.Įxample 2. The combinations we must check are ammonium nitrate and sodium sulfate.Īll nitrates and most sulfates are soluble, and sodium sulfate is not listed among the Will a precipitation occur upon mixing their aqueous solutions? For the two soluble compounds above, ammonium sulfate and sodium nitrate, Whether precipitation will occur when two solutions of different soluble ionic compounds are mixed.Įxample 1. The above table (or one similar to it) can be used to predict Soluble: solubility > 1 g / 100 g water Slightly soluble: 1 g / 100 g water ≥ solubility ≥ 0.01 g / 100 g water Insoluble: solubility < 0.01 g / 100 g water. Table 1: Solubility of ionic compounds in aqueous solution The solubility rules presented below are from Oxtoby, et al. The rules provide a quick qualitative check on the solubility of combinations of ions in water. These vary in detail, according to different sources, but broadly speaking The solvent molecules interact very strongly with the ions, which are said to be solvated.Ī simple set of rules, known as solubility rules,Īllows us to predict when a precipitation reaction will occur. All the other stoichiometric relationships are one-to-one. Note in particular that each formula unit of (NH 4) 2SO 4 Notice that dissociation equations express stoichiometric relationships. So for example, the dissociation equations for the soluble ionic compounds ammonium sulfate The number of atoms of each type and the net charge on each side of the equation must be the same. Of course, just like any other chemical equation, it must be balanced:

In this view, dissociation seems more like a physical change than a chemical change,īut we can still represent the process as a chemical equation. We call an ionic compound that dissociates in solution to give rise to mobile ions an This is why pure water does not conduct electricity well, but a solution of NaCl (for example) can.
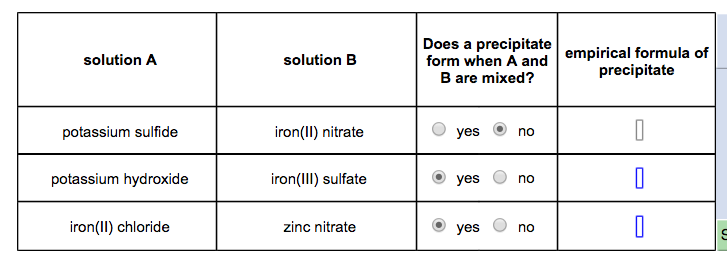
#When aqueous solutions of are mixed a precipitate forms free
Solid crystal lattice into individual ions that are free to move about in solution. When an ionic compound dissolves in water to form a solution, the compound dissociates into separated ions.įor most purposes, we can consider this dissociation as a separation of pre-existing ions from a The precipitate can be separated from the remaining solution by filtration.ĭissociation of ionic compounds in aqueous solution The cloudiness is due to the formation of small aggregations of solid substance (the precipitate). In such cases, the solution turns visibly cloudy, a phenomenon known as precipitation. When the ions present together in the mixture can form an insoluble compound. Writing molecular, complete ionic, and net ionic equations for a precipitation reaction.Ī precipitation reaction occurs upon the mixing of two Using solubility rules: Predicting when a precipitation reaction will occur. MgCl2 (aq) +KOH(aq) O C.GENERAL CHEMISTRY TOPICS Precipitation reactionsĭissociation of ionic compounds in aqueous solution. MgCl2 (aq) + KOH(aq) Mg(OH)2(s) + KCl(aq) х х He (aq), Part 4 (1 point) Which of these three reactions give clear visual evidence of the ion-exchange process? Choose one or more: O A.

Write a balanced net ionic equation for the following reaction. Remember to include states of matter in your equation. NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) - AgCl(s) + NaNO3(aq) X х He (aq), o

1st attempt Part 1 (1 point) I See Periodic Table See Hint Remember to include states of matter in your equation. The solubility rules can be used to predict the formation and identity of a precipitate. A precipitate may form when aqueous solutions of ionic compounds are mixed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
